Refresh token - secret gem for authentication

Beside access token, we also have refresh token. They're best friend forever, you need them to help your authentication mechanism to be more secure and reliable. So what is it?
Have you ever seen the alert like Your session has expired when use your app ? That's the signal of your access token has been expired. So may you ask the question...

Look like option A is fine and maybe, option C and D will work, MAYBE 🤣, but the better and common answer is Refresh token. So how to do it?
What is refresh token?
When a user logs in successfully, the server provides two tokens: an access token and a refresh token.
Think of the access token as your employee badge and the refresh token as your government ID card. Both prove who you are, but they serve different purposes and have different lifetimes.
-
Role: If your employee badge expires, you can use your ID card to request a new one. But you can’t use your badge to get a new ID card.
-
Lifetime: Your employee badge is short-lived and may expire quickly, while your ID card lasts much longer — though it can still be revoked if necessary.
Summary, refresh token is a token that is used to request a new access token when the current access token has expired. This mechanism ensures that the user stays logged in even if the access token expires.
How to use refresh token?
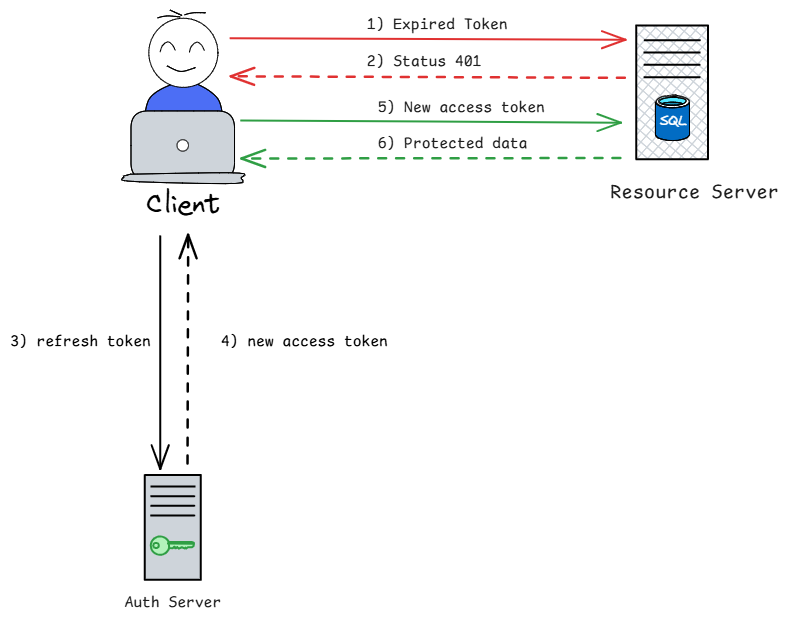
- App request with expired token
- Server return 401
- App use
refresh tokento request new token from server - Server verify
refresh tokenand return newaccess token - App use new
access tokento request resource - Server verify new
access tokenand return resource to app
Best practices
Life time
-
Access token: Keep it short, maybe around 5-10 mins, it ensure if the hacker can get it but can't use it forever
-
Refresh token: Because we use it to request new access token, so make it longer than access token, maybe 7-14 days, or even a month.
Token type
-
Access token: Use JWT for access token, because we can use
statelessproperty of it to make the authentication more faster. -
Refresh token: We can use opaque token or JWT, both are fine, but I prefer opaque token because it is easy to revoke. If we use JWT, we must to wait until the token expire or we need to create an black list to store invalid token, this thing violate the stateless property
Storage in client-side
-
Access token: Because it life time is short, so we can store it in
memoryorcookiewithout specify config. Save inmemorymaybe better because it prevent XSS attack, but it'll lost when user close or refresh the page -
Refresh token: Because it life time is longer, so I recommend store it in
cookiewithhttpOnlySameSite=strictorSameSite=LaxSecure
Never store refresh token in localStorage or sessionStorage, because it can be steal by XSS attack
Storage in server-side
-
Access Token: No need to store it in server
-
Refresh Token: We should hashing it before storing it in database.
We should return raw token (token before hashing) to client.
Refresh token rotation
Refresh token should be use only one time, it means when we use refresh token to get a new access token, we should revoke the old refresh token and return new refresh token to client.
This practice help to prevent the case when hacker have refresh token and use it to request new access token. When official user reuse old refresh token, the system can detect suspicious activity, from there we can take action to revoke every token related to this user.
Also, this make user who access usually never been logout and user who won't access for a long time will be logout.
Binding to specific user device
This make one more security step, it prevent the case when hacker get refresh token, but they can't use it if they don't have user device. We can make it by create an "fingerprint" for client which combine some information:
- IP address (optional): User's ip address
- Device id: An random string generated by server and store it in cookie with
Secure, SameSite=strict\lax. - User agent: Browser and OS information (it can't be fake if hacker know your user agent)
Fingerprint = IP + Device ID + User Agent
When client use refresh token to request new access token, we can use fingerprint to verify that the request is from the same client.
