Install ArgoCD via Helm + Harbor Registry + Jenkins CI/CD Pipeline
Now let's build a complete enterprise-grade setup: Harbor (private Docker registry) ← Jenkins (CI) ← ArgoCD (CD). Harbor replaces Docker Hub, keeping all your images private and safe. Jenkins builds and pushes to Harbor, ArgoCD pulls from Harbor to deploy. Perfect for on-premise or GCP environments.
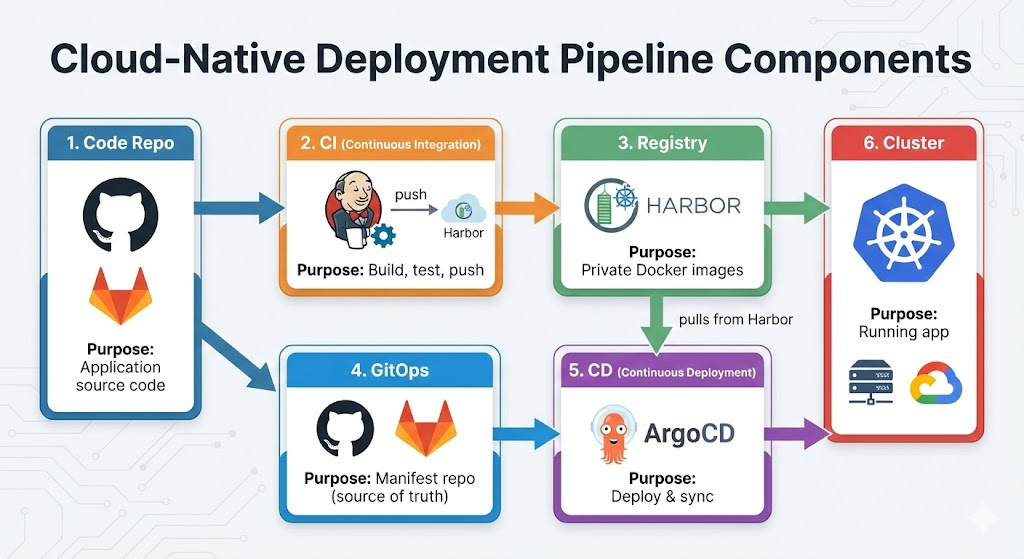
Step 1: Install Harbor via Helm (Private Docker Registry)
Harbor is your private Docker registry—like Docker Hub but running on your own Kubernetes cluster, with vulnerability scanning and access control built-in.
Add Harbor Helm Repo and Install
helm repo add harbor https://helm.goharbor.io
helm repo update
Create the Harbor namespace:
kubectl create namespace harbor
Install Harbor with minimal config (insecure for testing—use HTTPS in production):
helm install harbor harbor/harbor \
--namespace harbor \
--set expose.type=NodePort \
--set expose.tls.enabled=false \
--set externalURL=http://harbor.example.com \
--set harborAdminPassword=Harbor12345
Or if you're on localhost (testing):
helm install harbor harbor/harbor \
--namespace harbor \
--set expose.type=NodePort \
--set expose.tls.enabled=false \
--set externalURL=http://localhost:30003 \
--set harborAdminPassword=Harbor12345
Wait for all pods to be ready:
kubectl get pods -n harbor -w
You should see harbor-core, harbor-database, harbor-redis, harbor-registry, etc. all in Running status.
Get the Harbor access details:
kubectl get svc -n harbor
Find the NodePort for Harbor (usually something like 30003 for HTTP). Access Harbor UI at http://localhost:30003 (or your server IP).
Default credentials:
- Username:
admin - Password:
Harbor12345(or whatever you set)
Step 2: Create Harbor Project and User
- Log into Harbor UI at
http://harbor.example.com(or localhost:30003) - Click Projects → New Project
- Name it
myapp(or your app name) - Leave it Private (secure)
- Click OK
Now you have a private Harbor project at harbor.example.com/myapp.
Step 3: Test Harbor: Push a Sample Image
From any machine with Docker installed:
# Login to Harbor
docker login harbor.example.com
# Enter username: admin, password: Harbor12345
# Pull a sample image from Docker Hub
docker pull nginx:latest
# Tag it for your Harbor repo
docker tag nginx:latest harbor.example.com/myapp/nginx:v1.0
# Push to Harbor
docker push harbor.example.com/myapp/nginx:v1.0
In Harbor UI, go to Projects → myapp → Repositories, and you should see myapp/nginx with tag v1.0.
Step 4: Install ArgoCD via Helm (Not kubectl manifests)
Now install ArgoCD using Helm, which gives us more control over configuration.
Add ArgoCD Helm repo:
helm repo add argo https://argoproj.github.io/argo-helm
helm repo update
Create ArgoCD namespace:
kubectl create namespace argocd
Install ArgoCD with Helm:
helm install argocd argo/argo-cd \
--namespace argocd \
--set server.insecure=true \
--set server.service.type=LoadBalancer
Or for a simpler setup (NodePort instead of LoadBalancer):
helm install argocd argo/argo-cd \
--namespace argocd \
--set server.insecure=true \
--set server.service.type=NodePort
Wait for pods to be ready:
kubectl get pods -n argocd -w
Get the ArgoCD UI access:
If using LoadBalancer:
kubectl get svc argocd-server -n argocd
Copy the EXTERNAL-IP. Open https://<EXTERNAL-IP> in your browser.
If using NodePort:
kubectl get svc argocd-server -n argocd
# Find the port (e.g., 32145)
Open https://localhost:32145 (or your server IP:32145).
Get ArgoCD admin password:
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d; echo
Login with admin + this password.
Step 5: Create Kubernetes Secret for Harbor in ArgoCD
ArgoCD needs to know how to authenticate to Harbor to pull images from your private registry.
Create the secret in ArgoCD namespace:
kubectl create secret docker-registry harbor-secret \
--docker-server=harbor.example.com \
--docker-username=admin \
--docker-password=Harbor12345 \
-n argocd
For localhost/testing:
kubectl create secret docker-registry harbor-secret \
--docker-server=harbor.example.com:30003 \
--docker-username=admin \
--docker-password=Harbor12345 \
-n argocd
Verify the secret:
kubectl get secret harbor-secret -n argocd
Step 6: Create Jenkins Credentials for Harbor
Jenkins needs to push images to Harbor.
- Go to Jenkins Dashboard → Manage Jenkins → Manage Credentials
- Click Add Credentials
- Fill in:
- Kind:
Username with password - Username:
admin - Password:
Harbor12345 - ID:
harbor-credentials
- Kind:
- Click Create
Step 7: Create Updated Jenkinsfile (Build & Push to Harbor)
Here's a complete Jenkinsfile that:
- Clones app code
- Builds Docker image
- Pushes to Harbor (not Docker Hub)
- Updates GitOps repo with new image tag
pipeline {
agent any
environment {
HARBOR_HOST = 'harbor.example.com:30003' // Change to your Harbor URL
HARBOR_PROJECT = 'myapp'
HARBOR_REPO = "${HARBOR_HOST}/${HARBOR_PROJECT}"
IMAGE_TAG = "${BUILD_NUMBER}"
IMAGE_NAME = "${HARBOR_REPO}/myapp:${IMAGE_TAG}"
GITHUB_REPO = 'https://github.com/your-user/argocd-gitops-repo.git'
GITHUB_TOKEN = credentials('github-token')
}
stages {
stage('Checkout App Repo') {
steps {
checkout scm
}
}
stage('Build Docker Image') {
steps {
script {
sh 'docker build -t ${IMAGE_NAME} .'
}
}
}
stage('Push to Harbor') {
steps {
script {
withCredentials([usernamePassword(credentialsId: 'harbor-credentials',
usernameVariable: 'HARBOR_USER',
passwordVariable: 'HARBOR_PASSWORD')]) {
sh '''
echo $HARBOR_PASSWORD | docker login -u $HARBOR_USER --password-stdin $HARBOR_HOST
docker push ${IMAGE_NAME}
'''
}
}
}
}
stage('Update GitOps Repo') {
steps {
script {
sh '''
# Clone GitOps repo
git clone https://${GITHUB_TOKEN}@github.com/your-user/argocd-gitops-repo.git gitops
cd gitops
# Update image tag in deployment.yaml
sed -i "s|image: .*/myapp:.*|image: ${IMAGE_NAME}|g" deployment.yaml
# Commit and push
git config user.email "[email protected]"
git config user.name "Jenkins Bot"
git add deployment.yaml
git commit -m "Update image to ${IMAGE_NAME}"
git push https://${GITHUB_TOKEN}@github.com/your-user/argocd-gitops-repo.git main
'''
}
}
}
}
post {
success {
echo "✅ Image built, pushed to Harbor, GitOps repo updated. ArgoCD will auto-sync!"
}
failure {
echo "❌ Pipeline failed"
}
}
}
Key changes from before:
- Harbor host:
harbor.example.com:30003(change to your setup) - Harbor credentials: uses
harbor-credentialsfrom Jenkins - Image path:
harbor.example.com:30003/myapp/myapp:123instead of Docker Hub
Step 8: Set Up GitOps Repo with ArgoCD Integration
Make sure your GitOps repo has:
deployment.yaml:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: myapp
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: myapp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: myapp
spec:
imagePullSecrets:
- name: harbor-secret # Reference the Harbor secret
containers:
- name: myapp
image: harbor.example.com:30003/myapp/myapp:latest # Harbor image
ports:
- containerPort: 3000
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: myapp-svc
namespace: default
spec:
selector:
app: myapp
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 3000
type: LoadBalancer
Important: Include imagePullSecrets: - name: harbor-secret so Kubernetes knows to use the Harbor credentials when pulling the image.
Commit and push this to your GitOps repo.
Step 9: Register GitOps Repo in ArgoCD
Via CLI:
argocd app create myapp \
--repo https://github.com/your-user/argocd-gitops-repo.git \
--path . \
--dest-server https://kubernetes.default.svc \
--dest-namespace default \
--sync-policy automated
Via UI:
- Click + NEW APP in ArgoCD
- Fill in:
- Application Name:
myapp - Repository URL:
https://github.com/your-user/argocd-gitops-repo.git - Path:
. - Cluster URL:
https://kubernetes.default.svc - Namespace:
default - Sync Policy:
Automatic
- Application Name:
- Click CREATE
ArgoCD will now watch your GitOps repo and auto-sync when manifests change.
Step 10: Test the Full Pipeline
-
Make a code change in your app repo:
git add .
git commit -m "Update feature"
git push origin main -
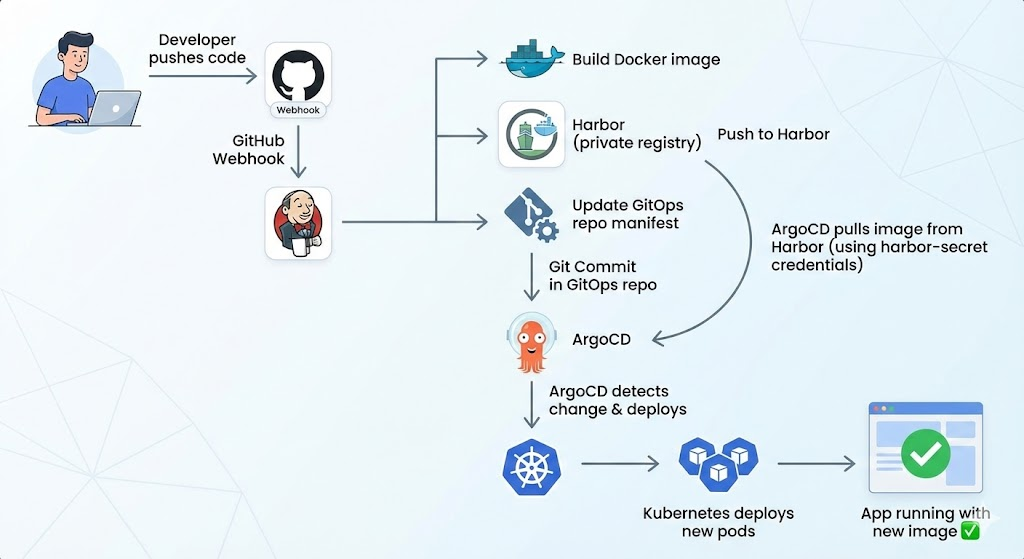
Watch Jenkins build:
- Webhook triggers Jenkins
- Jenkins builds Docker image
- Jenkins pushes to Harbor (
harbor.example.com:30003/myapp/myapp:123) - Jenkins updates
deployment.yamlin GitOps repo with new image tag
-
Watch ArgoCD sync:
- ArgoCD detects change in GitOps repo
- ArgoCD pulls new manifest
- ArgoCD pulls Docker image from Harbor (using
harbor-secret) - New pods spin up with image from Harbor
-
Verify deployment:
kubectl get pods
kubectl describe deployment myapp
kubectl logs -f deployment/myapp
Complete Architecture Diagram
Troubleshooting
1. Jenkins can't push to Harbor (Login failed):
- Verify Harbor is accessible:
curl http://harbor.example.com:30003 - Check Harbor credentials in Jenkins match actual username/password
- Verify
harbor-credentialsID exists in Jenkins
2. ArgoCD can't pull image from Harbor (ImagePullBackOff):
- Confirm
harbor-secretexists inargocdnamespace:kubectl get secret -n argocd - Verify secret has correct credentials:
kubectl get secret harbor-secret -n argocd -o yaml - Ensure
imagePullSecrets: - name: harbor-secretis in yourdeployment.yaml
3. Harbor image not found (404):
- Verify image was pushed: check Harbor UI or
docker search harbor.example.com/myapp - Confirm image tag matches between Jenkins Jenkinsfile and GitOps repo manifest
- Check Jenkins logs:
docker pushoutput should show success
4. ArgoCD sync keeps failing:
- Click app in ArgoCD UI and check "Conditions" for error messages
- Verify GitOps repo is accessible:
git clone https://github.com/your-user/argocd-gitops-repo.git - Check if manifest YAML is valid:
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml --dry-run
Best Practices
- Use HTTPS for Harbor in production — configure TLS certs and use proper domain
- Create Harbor users per team — don't share the admin account
- Enable image vulnerability scanning — Harbor can scan for CVEs automatically
- Use image tags, never
:latest— use${BUILD_NUMBER}for traceability - Separate app repo from GitOps repo — cleaner Git history
- Enable ArgoCD automatic sync — Git becomes the source of truth