ArgoCD + Jenkins: Complete GitOps CI/CD Pipeline
Let's combine the best of both worlds: Jenkins builds images, ArgoCD deploys them. Jenkins is fantastic at CI (build, test, push), but ArgoCD is the deployment king because it treats Git as the source of truth. Together they create a bulletproof pipeline: code commit → Jenkins builds → image pushed → Git manifest updated → ArgoCD syncs → app deployed, all automatically.
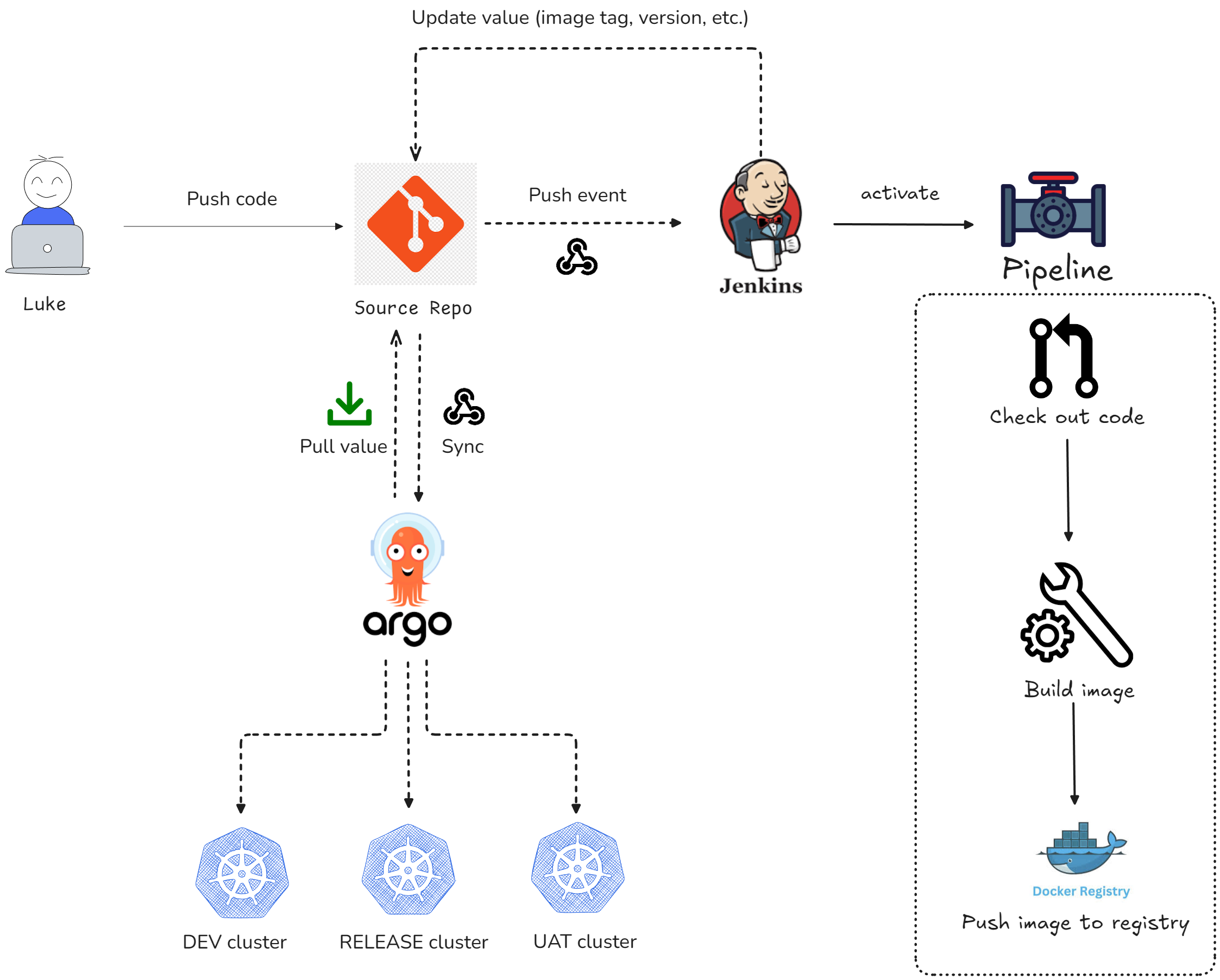
No manual deployments, no SSH-ing into servers, no kubectl apply commands. Pure GitOps automation.
The Flow: Jenkins → ArgoCD
Here's the complete journey:
- Developer pushes code to GitHub/GitLab
- Git webhook triggers Jenkins pipeline
- Jenkins:
- Clones the repo
- Builds a Docker image
- Pushes image to Docker Hub (or your registry)
- Updates the Kubernetes manifest (e.g.,
deployment.yaml) with the new image tag in Git
- ArgoCD detects the change in Git
- ArgoCD syncs the new manifest to Kubernetes
- New pods spin up with the new image
All automatic. Zero kubectl apply commands. This is GitOps done right.
Prerequisites
You already have:
- Jenkins installed (from the previous guide)
- ArgoCD installed (from the earlier guide)
- kubectl configured to talk to both Jenkins and ArgoCD clusters
- A GitHub/GitLab repo with your app code and
deployment.yaml
Step 1: Create a Git Repository for Kubernetes Manifests
You need two repos:
- Application repo — your actual code (Node.js, Java, Python, etc.)
- GitOps repo — only Kubernetes manifests (
deployment.yaml,service.yaml, etc.)
Create the GitOps repo (can be on GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket):
git clone https://github.com/your-user/argocd-gitops-repo.git
cd argocd-gitops-repo
Add a simple deployment.yaml:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: myapp
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: myapp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: myapp
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp
image: your-dockerhub-username/myapp:latest # Will be updated by Jenkins
ports:
- containerPort: 3000
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: myapp-svc
namespace: default
spec:
selector:
app: myapp
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 3000
type: LoadBalancer
Commit and push:
git add .
git commit -m "Initial K8s manifests"
git push origin main
Step 2: Set Up ArgoCD Application
ArgoCD will watch this GitOps repo and automatically sync when manifests change.
Via CLI:
argocd app create myapp \
--repo https://github.com/your-user/argocd-gitops-repo.git \
--path . \
--dest-server https://kubernetes.default.svc \
--dest-namespace default \
--sync-policy automated
The --sync-policy automated means ArgoCD will automatically deploy whenever Git changes.
Via UI:
- Click + NEW APP in ArgoCD
- Fill in:
- Application Name:
myapp - Repository URL:
https://github.com/your-user/argocd-gitops-repo.git - Path:
.(root of repo) - Cluster URL:
https://kubernetes.default.svc - Namespace:
default - Sync Policy:
Automatic
- Application Name:
- Click CREATE
Step 3: Create a Personal Access Token for Jenkins
Jenkins will need to push changes to the GitOps repo, so it needs credentials.
On GitHub:
- Go to Settings → Developer settings → Personal access tokens → Tokens (classic)
- Click Generate new token
- Give it:
- Name:
jenkins-gitops - Scopes: check
repo(full repo access) - Expiration: No expiration (or set as you like)
- Name:
- Copy the token (it looks like
ghp_xxxxxxxxxxxx)
On GitLab:
- Go to Settings → Access Tokens
- Create a token with
apiandwrite_repositoryscopes
Save this token securely—Jenkins will use it.
Step 4: Create Jenkins Pipeline with GitOps Integration
Create a new Pipeline job in Jenkins (or modify your existing one). Here's a sample Jenkinsfile that:
- Clones your app repo
- Builds a Docker image
- Pushes it to Docker Hub
- Updates the GitOps repo with the new image tag
pipeline {
agent any
environment {
DOCKER_HUB_USER = 'your-dockerhub-username'
DOCKER_HUB_PASS = credentials('docker-hub-password') // Jenkins credential
GITHUB_TOKEN = credentials('github-token') // Jenkins credential
GITHUB_REPO = 'https://github.com/your-user/argocd-gitops-repo.git'
IMAGE_TAG = "${BUILD_NUMBER}" // Use build number as tag
IMAGE_NAME = "${DOCKER_HUB_USER}/myapp:${IMAGE_TAG}"
}
stages {
stage('Checkout App Repo') {
steps {
checkout scm // Clones the app repo
}
}
stage('Build Docker Image') {
steps {
script {
sh 'docker build -t ${IMAGE_NAME} .'
}
}
}
stage('Push to Docker Hub') {
steps {
script {
sh '''
echo $DOCKER_HUB_PASS | docker login -u $DOCKER_HUB_USER --password-stdin
docker push ${IMAGE_NAME}
'''
}
}
}
stage('Update GitOps Repo') {
steps {
script {
sh '''
# Clone the GitOps repo
git clone https://${GITHUB_TOKEN}@github.com/your-user/argocd-gitops-repo.git gitops
cd gitops
# Update the image tag in deployment.yaml
sed -i "s|image: .*/myapp:.*|image: ${IMAGE_NAME}|g" deployment.yaml
# Commit and push
git config user.email "[email protected]"
git config user.name "Jenkins Bot"
git add deployment.yaml
git commit -m "Update image to ${IMAGE_NAME}"
git push https://${GITHUB_TOKEN}@github.com/your-user/argocd-gitops-repo.git main
'''
}
}
}
}
post {
success {
echo "✅ Image built and pushed, GitOps repo updated. ArgoCD will auto-sync!"
}
failure {
echo "❌ Pipeline failed"
}
}
}
Key points:
- Credentials: Store
docker-hub-passwordandgithub-tokenin Jenkins Credentials store - Image tag: Using
${BUILD_NUMBER}so each build gets a unique tag - sed command: Updates the image in
deployment.yaml(change the regex to match your file format) - Git push: Pushes the updated manifest back to the GitOps repo
Step 5: Store Credentials in Jenkins
Before running the pipeline, add your credentials to Jenkins:
- Go to Jenkins Dashboard → Manage Jenkins → Manage Credentials
- Click Add Credentials for each:
- docker-hub-password
- Kind: Secret text
- Secret: your Docker Hub password (or access token)
- ID:
docker-hub-password
- github-token
- Kind: Secret text
- Secret: the Personal Access Token from GitHub
- ID:
github-token
- docker-hub-password
Step 6: Set Up Git Webhook (Trigger Jenkins)
When you push code, Git should trigger the Jenkins pipeline (we covered this in the earlier guide).
On GitHub:
- Go to your application repo → Settings → Webhooks → Add webhook
- Payload URL:
https://jenkins.example.com/github-webhook/(or use ngrok for localhost) - Content type:
application/json - Events:
Just the push event - Click Add webhook
Now every git push to the app repo triggers Jenkins.
Step 7: Test the Full Pipeline
- Make a code change in your app repo (e.g., update a comment in the code)
- Commit and push:
git add .
git commit -m "Update feature"
git push origin main - Watch Jenkins build:
- GitHub sends webhook → Jenkins starts a build
- Jenkins builds the image
- Jenkins pushes to Docker Hub
- Jenkins updates
deployment.yamlin GitOps repo
- Watch ArgoCD sync:
- ArgoCD detects the change in GitOps repo (usually within 3 minutes, or immediately if you force sync)
- ArgoCD pulls the new manifest
- ArgoCD updates the Kubernetes Deployment
- New pods spin up with the new image
Verify in Kubernetes:
kubectl get pods
kubectl describe deployment myapp
You should see pods with the new image running.
Alternative: Trigger ArgoCD from Jenkins (Instead of Auto-Sync)
If you prefer manual control instead of auto-sync, have Jenkins directly trigger ArgoCD to sync after the image is pushed.
Add this stage to the Jenkinsfile:
stage('Sync with ArgoCD') {
steps {
script {
sh '''
argocd app sync myapp --force
argocd app wait myapp --timeout 600
'''
}
}
}
This tells ArgoCD to immediately sync the app after Jenkins finishes.
You'll need the argocd CLI installed on the Jenkins agent (or in a Jenkins Docker image).
Optional: ArgoCD Notifies Jenkins After Sync
You can also have ArgoCD notify Jenkins when a sync completes (good for post-deployment testing or notifications).
In ArgoCD, configure a webhook to call Jenkins:
kubectl edit configmap argocd-notifications-cm -n argocd
Add:
service.webhook.jenkins: |
url: http://jenkins:8080/job/myapp-post-deploy/build?token=SECRET_TOKEN
Then create a Jenkins job myapp-post-deploy that runs smoke tests or notifications.
Common Issues
1. Image doesn't update in Kubernetes:
- Check if Jenkins actually pushed the image:
docker image lson Docker Hub - Check if the GitOps repo was updated: look at Git commits
- Check ArgoCD sync status in the UI (may take a few minutes)
2. ArgoCD says "OutOfSync" but nothing changes:
- Click SYNC to manually trigger sync
- Or use:
argocd app sync myapp
3. Jenkins can't push to Git:
- Verify GitHub token has
reposcope:curl -H "Authorization: token TOKEN" https://api.github.com/user - Check Jenkins logs for git errors:
kubectl logs -n jenkins deploy/jenkins
4. Docker image push fails:
- Verify Docker Hub credentials are correct in Jenkins
- Check image name matches your Docker Hub repo name
Best Practices
- Never push credentials to Git—always use Jenkins secrets
- Use image tags, not
:latest—${BUILD_NUMBER}is good for traceability - Keep GitOps repo separate from app repo for cleaner Git history
- Enable ArgoCD automatic sync to be truly GitOps—Git becomes the source of truth
- Monitor both Jenkins and ArgoCD—watch logs for issues